The Diamond Lab
Leviev's Diamond Buying Guide
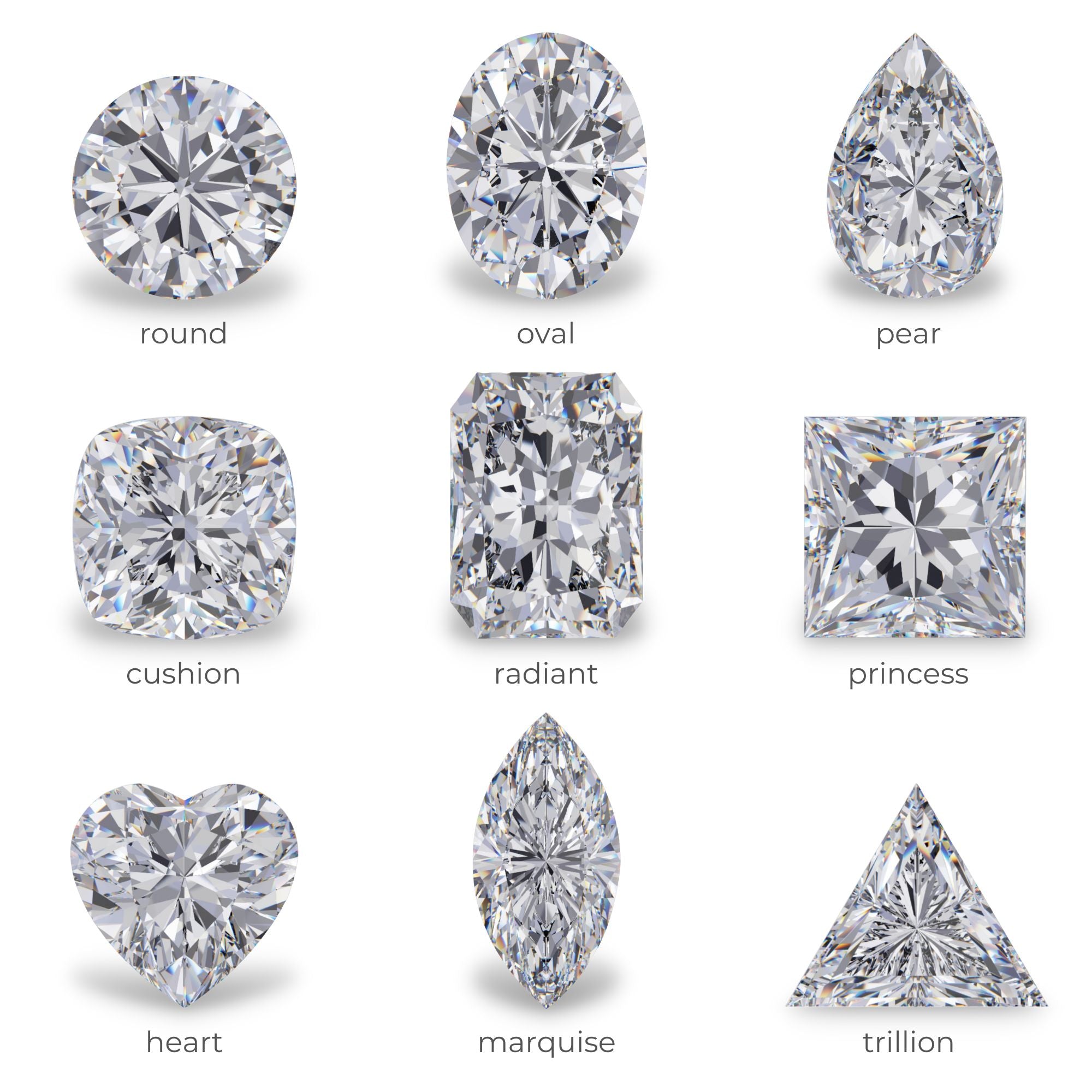
Intro To Diamonds
Diamond is the hardest natural material on earth. Formed deep within the Earth over a billion years ago and propelled to the surface by powerful volcanic eruptions, diamonds symbolize a timeless saga of pressure, perseverance, and sheer brilliance.
In This Guide
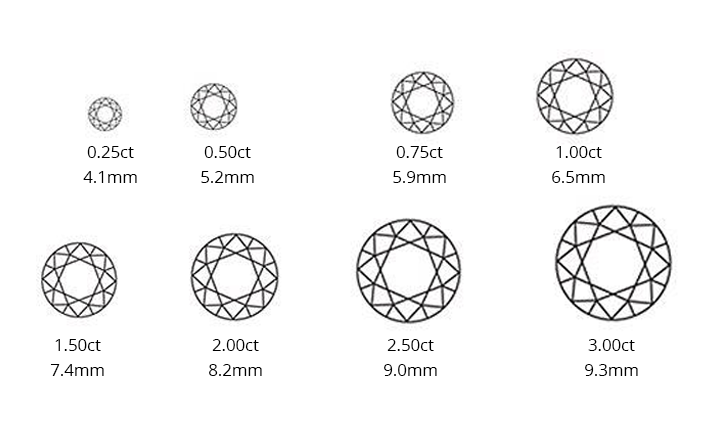
As you delve into our comprehensive diamond buying guide, you'll uncover the mystique and meticulous methodology behind grading these precious stones, exploring the renowned 4 Cs: color, cut, clarity, and carat weight.
Allow us to illuminate your path in selecting a diamond that sparkles while telling a story of nature, of love, and of unmatched elegance.